I think some wires got crossed in YouTube recently as IBM Service Management moved over to the IBM Cloud channel, and it appears that their most recent videos are hidden from any searches. However, thanks to Matt Duggan from IBM who shared the direct links on LinkedIn, I've added them all to my own IBM Agile Service Manager playlist, which can be found here:
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLxv2WlaeOSG9z_L4LCjHzz-qnZ-vDqnjn
Have fun
Thursday, June 29, 2017
Tuesday, June 27, 2017
IBM Netcool Agile Service Manager - What is swagger?
Introduction
The ASM documentation references "swagger" and "swagger URLs" for several different services. The purpose of this post is to describe what this actually means.
What is swagger?
Here's a statement from swagger.io:
The goal of Swagger™ is to define a standard, language-agnostic interface to RESTAPIs which allows both humans and computers to discover and understand the capabilities of the service without access to source code, documentation, or through network traffic inspection.
So the goal of this article is to show what that statement actually means to you in the context of Agile Service Manager.
Swagger URLs for ASM
There are 7 different services that are accessible via a browser. My ASM host is named "asm", and here are the URLs I have for the services:
File Observer Swagger UI
http://asm:9098/1.0/topology/observer/swagger/#/
topology-service Swagger UI
http://asm:8080/1.0/topology/swagger#/
search service Swagger UI
http://asm:7080/1.0/search/swagger
ITNM observer Swagger UI
http://asm:9080/1.0/topology/observer/swagger
OpenStack observer Swagger UI
http://asm:9082/1.0/topology/observer/swagger
Event observer Swagger UI
http://asm:9084/1.0/topology/observer/swagger
Docker observer Swagger UI
http://asm:9086/1.0/topology/observer/swagger
Topology Service
The Topology Service is the one that will be the one you normally want to visit to view (and even change) data about the resources in the ASM database. Here's what you'll see when you access the URL:
You can click on each section to see the operations associated with each. The section I like is Resources. Here are the operations found there:
From here, you can click on one of the operations, such as the first one: GET /resources. Here's just the first part of what's displayed there:
Notice that it gives you documentation about the operation and lots of other information. Specifically, it provides you with the ability to fill in values for all of the parameters that the operation accepts AND allows you to execute the operation! It also provides you with the 'curl' command that you can run from the command line to execute the exact same operation, with the exact same parameters.
The way to execute the operation is to click the "Try it out!" button at the bottom of the operation documentation.
And there you go! Some data. In this case, what's returned is the ID of the node in the topology that matches the criteria I specified. I can then take this ID and use it as input to other operations in this same group or in other groups.
Try it out and have fun
The above is just an short entry point into ASM's swagger UIs. Play around with them and you'll see that you can do some interesting stuff.
Monday, June 26, 2017
Agile Service Manager UI Introduction
Here's a short video introduction covering the basic features of IBM's Netcool Agile Service Manager.
IBM Netcool Agile Service Manager Thoughts
I recently installed IBM's Netcool Agile Service Manager and wanted to give my initial thoughts on it.
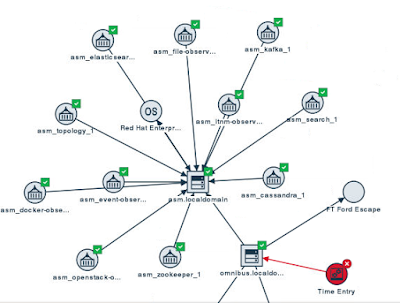
Basically, it's a real-time topology viewer for multiple technologies. Specifically, it can currently render topology data for ITNM, OpenStack and Docker, all in one place. Additionally, it maps events to the topology so you can see any events that are affecting a resource in the context of its topology. So, for example, if you receive a CRITICAL event for a particular Docker container, you will see the node representing that container turn red. Pretty neat. Here's an example of a 1-hop topology of my ASM server's docker infrastructure (you always have to start at some resource to view a topology):
Here's a screenshot where I've manually modified the topology using a combination of the File Observer and direct access to the Topology Service REST API (from the Swagger URL):
Notice also that Time Entry is in a Critical state. That's due to an event that I generated.
No, ASM is not a complete replacement for TBSM or TADDM, but you can definitely think of it as "TBSM Lite". TBSM still has some very unique features, such as status propagation, service rules, and custom KPIs that can be defined on a per-business-service basis.
And TADDM's unique capability is the hard work of actually discovering very detailed data and relationships in your environment.
However, because the search and visualization pieces of ASM are so fast and efficient, I can definitely see ASM being used as at least part of the visualization portion of TADDM. What would be required to allow this is a TADDM Observer to be written.
Additionally, I think the ASM database and topology will in the future be leveraged by TBSM, though this will take a little work.
What is Agile Service Manager?
Basically, it's a real-time topology viewer for multiple technologies. Specifically, it can currently render topology data for ITNM, OpenStack and Docker, all in one place. Additionally, it maps events to the topology so you can see any events that are affecting a resource in the context of its topology. So, for example, if you receive a CRITICAL event for a particular Docker container, you will see the node representing that container turn red. Pretty neat. Here's an example of a 1-hop topology of my ASM server's docker infrastructure (you always have to start at some resource to view a topology):
What's so great about it?
Combined Topology View
First, this topology view is wonderful for Operations and Development because it shows a topology view of your combined Network, Docker and Openstack environments, so everyone can see where applications are running and the dependencies among the pieces.ElasticSearch
Second, it's got ElasticSearch under the covers, so updates and searches are amazingly fast, and the topology view is built extremely quickly.Custom Topology Information
Third, you can add your own topology information to make it even more useful!Here's a screenshot where I've manually modified the topology using a combination of the File Observer and direct access to the Topology Service REST API (from the Swagger URL):
Notice also that Time Entry is in a Critical state. That's due to an event that I generated.
History
Fourth, it maintains history about the topology. That means that you can view the difference in topology between 2 hours (or two days) ago and right now.Is ASM a complete replacement for TBSM and/or TADDM?
No, ASM is not a complete replacement for TBSM or TADDM, but you can definitely think of it as "TBSM Lite". TBSM still has some very unique features, such as status propagation, service rules, and custom KPIs that can be defined on a per-business-service basis.
And TADDM's unique capability is the hard work of actually discovering very detailed data and relationships in your environment.
However, because the search and visualization pieces of ASM are so fast and efficient, I can definitely see ASM being used as at least part of the visualization portion of TADDM. What would be required to allow this is a TADDM Observer to be written.
Additionally, I think the ASM database and topology will in the future be leveraged by TBSM, though this will take a little work.
Parting thoughts
ASM is a truly useful product, with some great capabilities. It's also incredibly easy to install if you've already got Netcool Operations Insight (or at least DASH) installed - I was able to get it installed in just a few hours. I'm certain IBM will be adding features and add-ons to provide even more functionality in the coming months.
Thursday, May 25, 2017
New Linux Samba vulnerability and fix
A new vulnerability was found in Linux Samba from version 3.5 and above. Details here:
https://www.samba.org/samba/security/CVE-2017-7494.html
The workaround is easy and is contained in the link above:
in your /etc/samba/smb.conf file, add the following in the [global] section:
https://www.samba.org/samba/security/CVE-2017-7494.html
The workaround is easy and is contained in the link above:
in your /etc/samba/smb.conf file, add the following in the [global] section:
nt pipe support = no
Then restart smbd with 'service smb restart'
Monday, April 24, 2017
BMXAA7025E and BMXAA8313E Errors running MAXINST on ICD 7.6
I wanted to install the demo data that's provided with ICD 76 by basically following the instructions found here:
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/community/wikis/home?lang=en#!/wiki/Anything%20about%20Tivoli/page/To%20load%20the%20sample%20DB2%20database%20after%20Control%20Desk%207.6%20installed
But I didn't find those steps before I started, so I took my own path.
Specifically, I didn't drop the database, and that meant that I encountered errors BMXAA7025E and BMXAA8313E when running the 'maxinst.sh' script. What I found is that the cleandb operation doesn't really delete all of the tables and views in the MAXIMO schema (I'm on DB2/WebSphere/RHEL 6.5), so when maxinst gets to running the files under:
/opt/IBM/SMP/maximo/tools/maximo/en/dis_cms
It fails because a few of these SQL files try to create tables and views that still exist. I found this link about the problem:
https://www-01.ibm.com/support/docview.wss?uid=swg21647350
But I didn't like it because it tells you to re-create the database. So with a little digging, I found that after I hit the error, I could run the following db2 commands to delete all of the tables and views that were not automatically deleted:
db2 connect to maxdb76 user maximo using passw0rd
db2 DROP TABLE ALIASES
db2 DROP TABLE ATTRIBUTE_TYPES
db2 DROP TABLE BNDLVALS
db2 DROP TABLE BUNDLENM
db2 DROP TABLE CDM_VERSION
db2 DROP TABLE CHANGE_EVENTS
db2 DROP TABLE CLASS_TYPES
db2 DROP TABLE CMSTREE
db2 DROP TABLE CMSTREES
db2 DROP TABLE DESIRED_SUPPORTED_ATTRS
db2 DROP TABLE DESIRED_SUPPORTED_MAP
db2 DROP TABLE ENUMERATIONS
db2 DROP TABLE FTEXPRSN
db2 DROP TABLE FTVALUES
db2 DROP TABLE INTERFACE_TYPES
db2 DROP TABLE LAPARAMS
db2 DROP TABLE LCHENTR
db2 DROP TABLE LCHENTRY
db2 DROP TABLE ME_ATTRIBUTES
db2 DROP TABLE METADATA_ASSN
db2 DROP TABLE MSS
db2 DROP TABLE MSS_ME
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/community/wikis/home?lang=en#!/wiki/Anything%20about%20Tivoli/page/To%20load%20the%20sample%20DB2%20database%20after%20Control%20Desk%207.6%20installed
But I didn't find those steps before I started, so I took my own path.
Specifically, I didn't drop the database, and that meant that I encountered errors BMXAA7025E and BMXAA8313E when running the 'maxinst.sh' script. What I found is that the cleandb operation doesn't really delete all of the tables and views in the MAXIMO schema (I'm on DB2/WebSphere/RHEL 6.5), so when maxinst gets to running the files under:
/opt/IBM/SMP/maximo/tools/maximo/en/dis_cms
It fails because a few of these SQL files try to create tables and views that still exist. I found this link about the problem:
https://www-01.ibm.com/support/docview.wss?uid=swg21647350
But I didn't like it because it tells you to re-create the database. So with a little digging, I found that after I hit the error, I could run the following db2 commands to delete all of the tables and views that were not automatically deleted:
db2 connect to maxdb76 user maximo using passw0rd
db2 DROP TABLE ALIASES
db2 DROP TABLE ATTRIBUTE_TYPES
db2 DROP TABLE BNDLVALS
db2 DROP TABLE BUNDLENM
db2 DROP TABLE CDM_VERSION
db2 DROP TABLE CHANGE_EVENTS
db2 DROP TABLE CLASS_TYPES
db2 DROP TABLE CMSTREE
db2 DROP TABLE CMSTREES
db2 DROP TABLE DESIRED_SUPPORTED_ATTRS
db2 DROP TABLE DESIRED_SUPPORTED_MAP
db2 DROP TABLE ENUMERATIONS
db2 DROP TABLE FTEXPRSN
db2 DROP TABLE FTVALUES
db2 DROP TABLE INTERFACE_TYPES
db2 DROP TABLE LAPARAMS
db2 DROP TABLE LCHENTR
db2 DROP TABLE LCHENTRY
db2 DROP TABLE ME_ATTRIBUTES
db2 DROP TABLE METADATA_ASSN
db2 DROP TABLE MSS
db2 DROP TABLE MSS_ME
db2 DROP TABLE MSS_RELATIONSHIPS
db2 DROP TABLE NAMING_IDENTIFIERS
db2 DROP TABLE NAMING_POLICIES
db2 DROP TABLE NAMING_RULES
db2 DROP TABLE RELATIONSHIPS
db2 DROP TABLE RELATIONSHIP_TYPES
db2 DROP TABLE SBSTVALS
db2 DROP TABLE SUPERIORS
db2 DROP TABLE VALID_REL_TYPES
db2 DROP VIEW ATTR_PRIORITIES
db2 commit
And then I could re-run the maxinst.sh script and it worked like a champ. Please feel free to use my super secure password for yourself.
Monday, April 3, 2017
DevOps: Operations Can't Fail
Agile and DevOps are all about "Fail Fast", which is fine for developers, but absolutely unacceptable for Operations.
For a recent example, just look at the recent AWS outage:
http://www.recode.net/2017/3/2/14792636/amazon-aws-internet-outage-cause-human-error-incorrect-command
That was caused by someone debugging an application. None of us want our Operations department to be in that position, but it can obviously happen. I think there are one or more reasons behind why it happened, and I've got some opinions on how we need to work to ensure it doesn't happen to us:
For a recent example, just look at the recent AWS outage:
http://www.recode.net/2017/3/2/14792636/amazon-aws-internet-outage-cause-human-error-incorrect-command
That was caused by someone debugging an application. None of us want our Operations department to be in that position, but it can obviously happen. I think there are one or more reasons behind why it happened, and I've got some opinions on how we need to work to ensure it doesn't happen to us:
Problem: Developers think Operations is easy
Absolutely everything labeled "DevOps" is aimed at allowing Development to do just enough "operations" to get by. But we in Operations know that it takes a lot more: Change and Configuration Management, Event Management, Business Service Modeling, and the list goes on and on. Individual Development teams don't necessarily understand these practices outside of their own application.
One Solution: We need to learn about "the new stuff"
The only way we'll be invited to the table to talk to development teams is to learn about the tools they're using (Jira, Puppet/Chef, Kubernetes, Docker, etc.). This will allow us to use a similar vocabulary when meeting with them. Without this basic knowledge, they simply won't invite us to any of their discussions.
Problem: Developers think Operations is unnecessary
Individual Development teams often don't see why the Operations department even exists. They have their tools that allow them to consistently deploy their application, so why does Operations need to be involved. They don't understand that any one of their 20-or-so "incidental" microservices may actually be absolutely critical to some other application in the environment.
One Solution: After learning the new stuff, ask to be involved
The Operations Manager needs to get involved with the Development teams. She needs to give Development teams some type of framework or process or SOMETHING that makes their application's metrics and availability visible to the Enterprise. This will allow ALL involved parties to understand the situation when there is an outage.
A great graphic from Ingo Averdunk at IBM
The parts in light blue (Logging, Monitoring, Event Mgmt, Notification, Runbook Automation, ChatOps and Root Cause Analysis) are those components that need to be standardized across all applications. If your Operations team isn't meeting with Development, you won't get to explain the need for the standard suite of tools.
There are other problems and other solutions
This post is meant to help Operations in a sea of DevOps information that is aimed only at Development, in the hope that we can reign things in and continue to ensure that the entire enterprise is healthy and available.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)